How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which covers essential aspects like pre-flight checks and maneuvering techniques. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
We will explore the intricacies of drone flight, covering essential aspects like understanding your drone’s controls, navigating using GPS and visual cues, and mastering various flight techniques. We’ll also delve into the art of capturing stunning aerial photos and videos, optimizing camera settings, and employing creative composition techniques. Beyond the technical aspects, we’ll address crucial safety protocols, legal compliance, and essential maintenance practices, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable drone experience.
Learning to fly a drone involves understanding its controls and safety procedures. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which includes pre-flight checks and understanding airspace regulations. For a comprehensive guide on the subject, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and responsible operation. Mastering these fundamentals will allow you to confidently navigate and control your drone effectively.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before embarking on any drone flight, a comprehensive pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents, damage to property, and legal repercussions. A thorough pre-flight inspection ensures your drone is in optimal condition and reduces the risk of unforeseen issues during flight.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
A thorough pre-flight inspection involves several key steps to ensure the drone’s airworthiness. These steps should become second nature before each flight.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the drone’s body, propellers, and landing gear for any visible damage, cracks, or loose parts. Check the camera and gimbal for proper functionality.
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for the planned flight duration. Ensure the battery is securely connected and free from any damage.
- GPS Signal: Allow ample time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff. A weak signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and flight instability.
- Calibration: Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) according to the drone’s manufacturer’s instructions. This ensures accurate flight control.
- Controller Check: Ensure the remote controller is fully charged and properly connected to the drone. Test the responsiveness of the control sticks and buttons.
- Software Update: Check for and install any available firmware updates for both the drone and the controller. Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements.
Safety Considerations for Drone Operation
Operating a drone safely involves awareness of environmental factors and legal restrictions. Ignoring these factors can have serious consequences.
| Weather Conditions | Airspace Restrictions | Obstacles | Emergency Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, snow, or fog. High winds can easily damage the drone and make control difficult. Inclement weather reduces visibility and can cause unexpected turbulence. | Familiarize yourself with local airspace regulations and restrictions. Many areas have designated no-fly zones near airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Check apps like B4UFLY or AirMap. | Be mindful of surrounding obstacles, such as trees, buildings, power lines, and people. Maintain a safe distance from these obstacles during flight. | Have a plan for handling emergencies, such as sudden battery failure or loss of signal. Know how to perform an emergency landing and how to recover the drone if it crashes. |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation is crucial for safe and efficient operation. This section will cover the basics of drone control and introduce different flight modes.
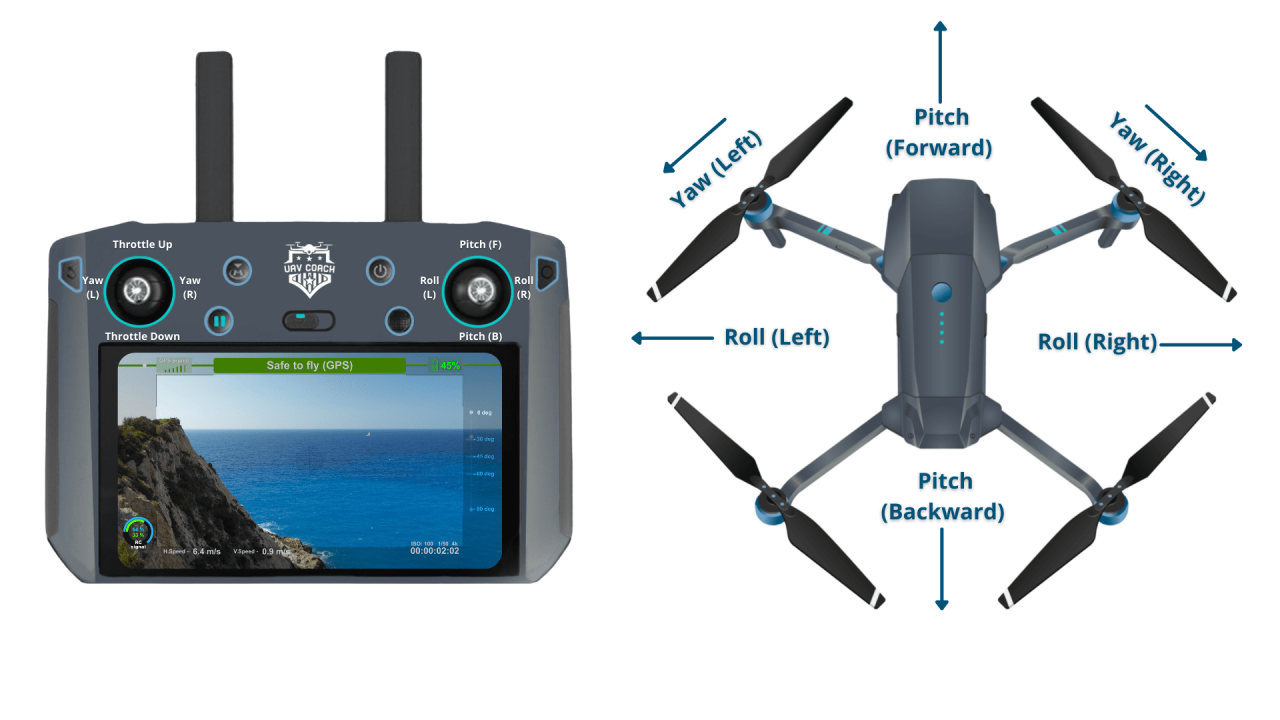
Drone Controls
Most drones utilize two control sticks on the remote controller. One stick controls the drone’s altitude and movement forward/backward, while the other controls its yaw (rotation) and lateral movement (left/right). Buttons on the controller are used for additional functions like taking photos, starting/stopping recording, and changing flight modes. Different drones might have slightly different control schemes, so always consult your drone’s manual.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer different flight modes to cater to various skill levels and situations. Beginner mode often limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, providing a more stable and forgiving flying experience. Sport mode typically unlocks higher speeds and more agile maneuvers, requiring greater skill and precision. GPS-based modes provide automated features like return-to-home (RTH).
Drone Navigation
Navigation involves using a combination of GPS and visual cues. GPS provides accurate positioning data, allowing the drone to maintain its location and return to the home point. Visual cues are crucial for avoiding obstacles and maintaining situational awareness, especially in areas with weak GPS signals. Always keep a visual line of sight with your drone.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Safe takeoff and landing are fundamental aspects of drone operation. Following a structured procedure minimizes the risk of accidents.
- Pre-flight Checks: Complete all pre-flight checks before attempting takeoff.
- Level Ground: Select a level and open area for takeoff and landing, away from obstacles.
- Slow Ascent: Ascend slowly and steadily, maintaining visual contact with the drone.
- Stable Hover: Practice hovering the drone in place before attempting any maneuvers.
- Controlled Descent: Descend slowly and steadily for landing.
- Gentle Touchdown: Aim for a gentle touchdown on a level surface.
Mastering Drone Flight Techniques
Proficiency in drone flight involves mastering various maneuvers and maintaining stable flight. This section will explore key flight techniques and common beginner mistakes.
Drone Flight Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include hovering (maintaining a fixed position), ascending (increasing altitude), descending (decreasing altitude), and turning (rotating the drone). More advanced maneuvers involve combinations of these basic movements, such as flying sideways, diagonally, or performing controlled rotations.
Maintaining Stable Flight
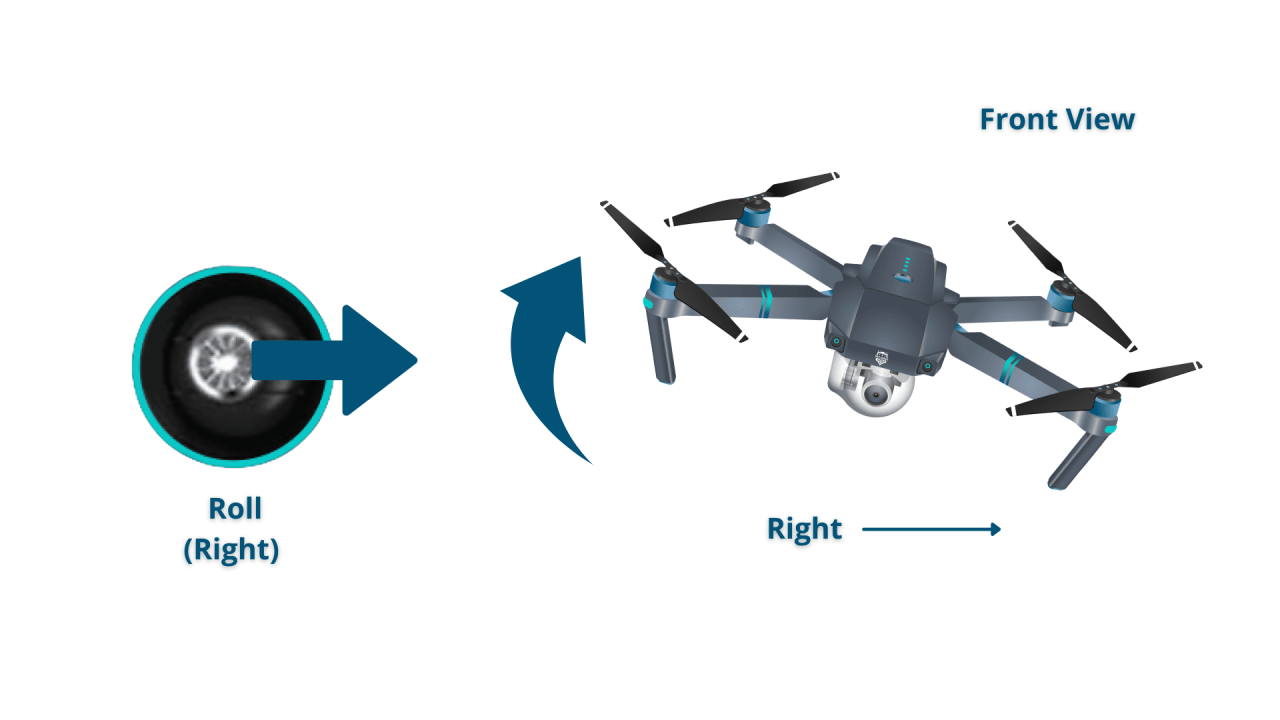
Stable flight requires smooth and precise control inputs. Avoid abrupt movements of the control sticks, especially in windy conditions. Practice maintaining a steady hover and gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers as your skills improve.
Drone Control Techniques in Various Situations
Different situations require different control techniques. In windy conditions, you’ll need to compensate for wind gusts by making small, corrective adjustments to maintain stability. In confined spaces, precise control and careful obstacle avoidance are essential.
Common Beginner Mistakes
Beginners often make several common mistakes that can lead to crashes or accidents. Avoiding these mistakes will improve safety and flight performance.
- Ignoring pre-flight checks: Always perform a thorough pre-flight check before each flight.
- Flying in adverse weather conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Losing visual line of sight: Always maintain visual contact with your drone.
- Flying too close to obstacles: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles.
- Overestimating your skills: Start with basic maneuvers and gradually increase the complexity as your skills improve.
- Ignoring battery level: Monitor the battery level closely and land the drone before the battery runs out.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section will explore how to achieve optimal results.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
High-quality aerial footage depends on several factors, including proper camera settings, stable flight, and good composition. Experiment with different settings and angles to find what works best for your subject and lighting conditions.
Composition and Framing
Good composition is crucial for visually appealing aerial shots. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques can enhance the impact of your photos and videos. Consider the background and foreground elements to create a balanced and visually interesting composition.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO affect the exposure and overall quality of your images and videos. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO controls sensitivity to light. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance for your shooting conditions.
Tips for Capturing Different Types of Aerial Footage
Different types of aerial footage require different techniques. Time-lapses require a stable platform and precise timing, while cinematic shots often involve smooth, controlled movements and creative camera angles.
- Time-lapses: Use intervalometer functionality for consistent time intervals between shots.
- Cinematic shots: Use smooth, controlled movements and creative camera angles to create a dynamic and visually appealing shot.
- Aerial panoramas: Stitch together multiple shots to create a wide-angle panoramic view.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for keeping your drone in good working order and preventing malfunctions. This section will cover routine maintenance tasks and troubleshooting common problems.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance helps to extend the lifespan of your drone and prevent unexpected issues. A proactive approach to maintenance will save you time and money in the long run.
| Task | Frequency | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propeller Inspection | Before each flight | Check for damage, cracks, or bends. Replace damaged propellers immediately. | Damaged propellers can cause instability and crashes. |
| Body Cleaning | After each flight | Clean the drone’s body with a soft cloth to remove dirt and debris. | Dirt and debris can interfere with sensors and mechanisms. |
| Battery Care | Regularly | Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries. | Proper battery care extends battery life and prevents damage. |
| Gimbal Check | Before each flight | Check for smooth movement and proper functionality. | A malfunctioning gimbal can affect image quality. |
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Several common drone malfunctions can be easily resolved with basic troubleshooting steps. Understanding these problems and their solutions will help you keep your drone flying smoothly.
- Low Battery: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with a clear view of the sky and wait for the GPS signal to reacquire.
- Propeller Failure: Replace the damaged propeller and check for other potential issues.
- Camera Malfunction: Check the camera settings and connections. If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and laws. This section will highlight important legal and regulatory considerations.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. These regulations often cover areas such as registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Drone Registration
In many jurisdictions, drone registration is mandatory. The registration process typically involves providing information about the drone and its owner. Failure to register your drone can result in fines or other penalties.
Airspace Restrictions and Privacy Concerns
Respecting airspace restrictions and privacy concerns is crucial for responsible drone operation. Avoid flying near airports, military bases, or other sensitive areas. Always obtain permission before flying over private property and respect individuals’ privacy.
Situations Where Drone Operation Might Be Prohibited
Several situations prohibit drone operation, including flying near emergency response areas, flying over crowds, or flying in areas with restricted airspace. Always prioritize safety and comply with all applicable regulations.
Advanced Drone Features and Capabilities
Modern drones offer a range of advanced features and capabilities, enhancing their functionality and performance. This section will explore some of these advanced features.
Advanced Features
Many advanced drones incorporate features like obstacle avoidance, autonomous flight modes (e.g., waypoint missions), and sophisticated camera systems. These features significantly enhance the drone’s capabilities and safety.
Different Drone Types
Various drone types cater to different needs and applications. Racing drones prioritize speed and maneuverability, while photography drones emphasize image quality and stability. Choosing the right drone depends on your specific requirements and budget.
Drone Battery Types
Different types of drone batteries offer varying flight times and performance characteristics. LiPo (Lithium Polymer) batteries are commonly used, but their characteristics (voltage, capacity) vary. Consider flight time requirements and charging capabilities when selecting batteries.
Advanced Features and Their Applications
Advanced features offer practical applications across various fields. Obstacle avoidance enhances safety, autonomous flight modes improve efficiency, and advanced camera systems enable high-quality image capture.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Improves safety by automatically avoiding obstacles during flight.
- Autonomous Flight Modes: Allows for pre-programmed flight paths and automated maneuvers.
- Advanced Camera Systems: Enables high-quality image and video capture with features like zoom, stabilization, and HDR.
Emergency Procedures and Safe Landing Techniques
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section will Artikel emergency procedures and safe landing techniques.
Emergency Procedures
In case of a drone malfunction or emergency, immediate action is necessary. Prioritize safety and follow a structured procedure to minimize damage and ensure a safe outcome.
Safe Emergency Landing
A safe emergency landing involves selecting a suitable landing area, initiating a controlled descent, and ensuring a gentle touchdown. The specific procedure will depend on the situation and the drone’s capabilities.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
If a crash occurs, carefully inspect the drone for damage before attempting to repair or replace parts. Prioritize safety and take appropriate precautions when handling damaged components.
Handling Low-Battery Situations, How to operate a drone
A low-battery situation requires immediate action to prevent a mid-air power failure. Initiate a return-to-home (RTH) function if available or perform a controlled descent to the nearest safe landing area.
Drone Software and Apps
Drone software and apps provide essential tools for controlling, managing, and analyzing drone data. This section will explore popular software and apps and their key features.
Drone Software and App Functions
Drone software and apps offer a wide range of functionalities, including flight control, camera settings adjustments, data logging, and flight planning. These tools enhance the drone’s capabilities and streamline the overall flying experience.
Controlling Drones and Managing Settings

Most drone apps allow for real-time control of the drone, enabling adjustments to flight parameters, camera settings, and other functionalities. The user interface typically provides intuitive controls and displays critical flight information.
Analyzing Flight Data and Logs
Drone software and apps often provide tools for analyzing flight data and logs, enabling users to review flight performance, identify potential issues, and optimize future flights. This data can be invaluable for improving flight skills and troubleshooting problems.
Popular Drone Software and Apps

Several popular drone software and apps are available, each offering a unique set of features and capabilities. Choosing the right software or app depends on your drone model and your specific needs.
- DJI Fly: DJI’s official app for controlling DJI drones.
- Litchi: A popular third-party app offering advanced flight planning and autonomous features.
- DroneDeploy: A platform for managing drone missions and processing aerial data.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible practice. By diligently following pre-flight procedures, understanding your drone’s capabilities, and adhering to all legal regulations, you can safely explore the boundless possibilities of aerial flight. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and confident drone pilot. So, get ready to take flight and capture your world from a whole new perspective!
FAQ Resource
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes and GPS assistance are available. Research models known for their stability and ease of use.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point. However, maintaining visual contact is crucial.
How do I clean my drone?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe down the drone’s body. Avoid using water or harsh chemicals. Consult your drone’s manual for specific cleaning instructions.
